Liability definition
/What is a Liability?
A liability is a legally binding obligation payable to another entity. Liabilities are incurred in order to fund the ongoing activities of a business. Examples of liabilities are accounts payable, accrued expenses, wages payable, and taxes payable. These obligations are eventually settled through the transfer of cash or other assets to the other party. They may also be written off through bankruptcy proceedings.
Accounting for Liabilities
Recording a liability requires a debit to an asset or expense account (depending on the nature of the transaction), and a credit to the applicable liability account. When a liability is eventually settled, debit the liability account and credit the cash account from which the payment came.
Presentation of Liabilities
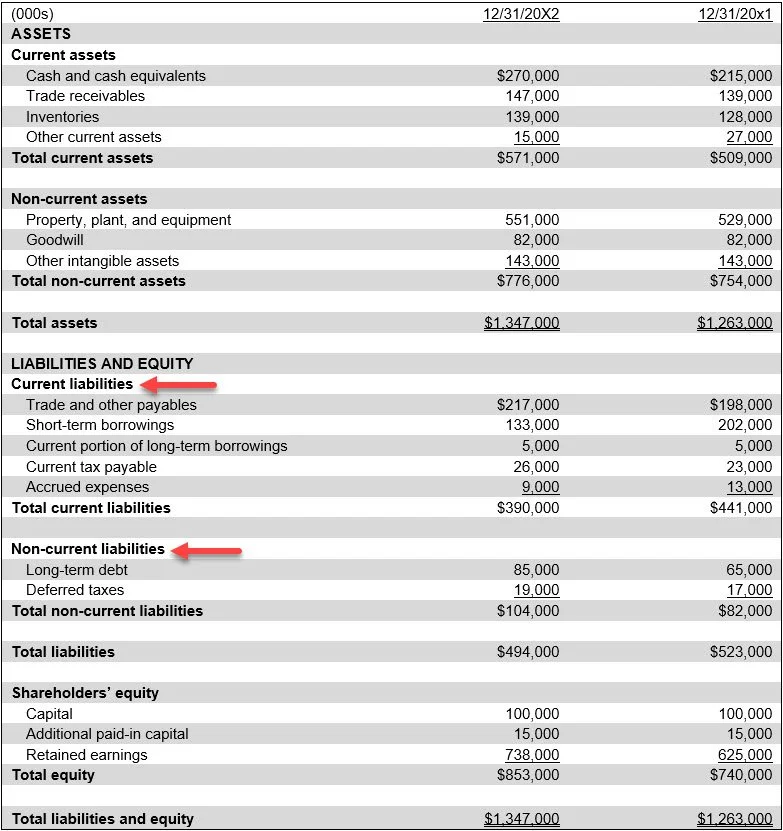
Liabilities expected to be settled within one year are classified as current liabilities on the balance sheet. All other liabilities are classified as long-term liabilities or non-current liabilities on the balance sheet. These two classifications appear in the following example balance sheet.
FAQs
What is a Contingent Liability?
A contingent liability is a potential financial obligation that may arise depending on the outcome of a future event, such as a lawsuit, warranty claim, or pending investigation. It is not recorded as an actual liability on the balance sheet unless the likelihood of the obligation is probable and the amount can be reasonably estimated. If the likelihood is possible but not probable, the liability is disclosed in the financial statement notes instead. This approach ensures transparency while avoiding the overstatement of liabilities that may never materialize.